Sep 22, 2019
During production of parts in the plastic industry, it is important to meet certain tolerances, eg. given in the drawing.
For this purpose regular checks of specific characteristics of a sample, mostly at multiple parts, are carried out in practice.
The control chart is a curve, which shows for example the mean of the samples and its standard deviation.
Limit values can be added into the control chart for warnings and necessary interventions. If these limits are exceeded, measures or interventions in the process can or must be taken.

Quality: Example of a Control Chart from the QM- Control Center in “solvtec
CAQ”
Related topics:
This information and services are provided by:

This glossary of plastic industry is provided by PLEXPERT Canada Inc.
Feb 1, 2022
To indicate on technical drawings that a shell surface must lie between two coaxial cylinders, the symbol of the cylindrical shape is indicated.
No reference point is described but only the radial distance between two coaxial cylinders, which are placed around the toleranced shell surface.
Cylindricity is a form tolerance.
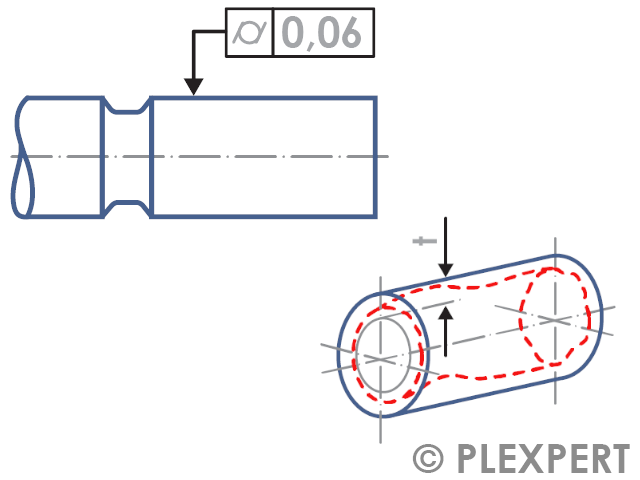
Quality Assurance: Tolerated shell surface with a distance of the imaginary cylinders of 0.06mm
Related topics:
This glossary of plastic industry is provided by PLEXPERT Canada Inc.
Nov 30, 2021
Following „first-time-right” principles, a Design for Manufacturing analysis (DFM) is an essential part of a successful product development and industrialization.
DFM describe a study where, the part design is screened and checked in full depth.
Only part designs fit for the selected manufacturing process shall enter industrialization.
All critical to quality (CTQ) part characteristics should be able to be produced within a reliable processing window and at lowest processing costs possible.
Lately also sustainability is getting more and more attention and the DFM-study is also including sustainability objectives.
A DFM is including also injection moulding simulations.
With this filling- , warpage- and cooling-simulation and can be extended to a CAE-based DOE.
Quality:
CAD design with critical sections identified
Quality Assurance: Detailed information about critical section (wall thickness too high)
Related Topics:
First-time-right
This glossary of plastic industry is provided by PLEXPERT Canada Inc.
Oct 6, 2019
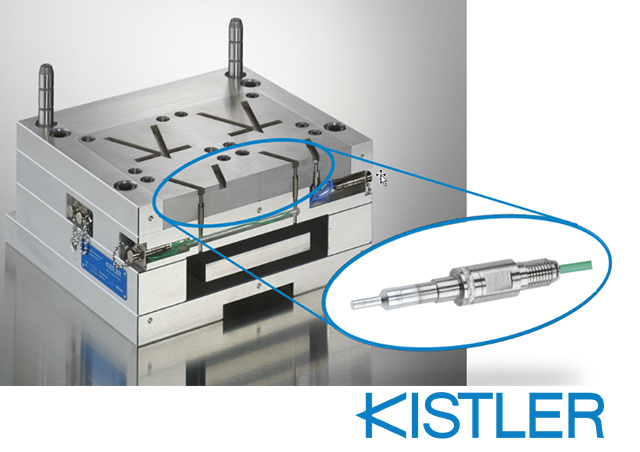
Cavity pressure can be determined directly, indirectly and contact-free.
Cavity pressure sensors are mostly Piezoelectric Sensors. The directed deformation of a piezoelectric crystal creates an electrical charge. The charge signal, which is proportional to the pressure, is converted into electrical voltage using a charge amplifier. Highly dynamic pressure progressions can be measured using this technology.
Direct-measuring sensors are in contact with the melt in the cavity, and they measure the pressure without transmission pins. These sensors provide also a very wide pressure range and a very robust design of the sensor.
An advantage of direct pressure sensors is the very accurate measurement of the cavity pressure. On many sensors, the front can be adapted to the surface of the cavity so that no mark can be seen on the part. Combined pressure/temperature sensors measure the cavity pressure and the contact temperature at the same point on the part.
Jul 17, 2019
A statistical experimental design, with specific information about the experiments, needs to be provided in advance to reach an optimized result.
This process is called DoE – Design of Experiments.
In order to save resources, statistical methods are used to reduce the effort between carrying out tests in relation to the accuracy of the obtained results.
For this one or more aims are set. In injection molding, this might be cycle time reduction, lower warpage, …
The changeable factors (injection time, melt temperature, packing pressure…) and their allowed range will be set as well.
On this base, an experimental design is created. It describes which experiments are to be carried out in which order.
The results of each experiment are determined for a final evaluation.
After the DoE, the information about how much each factor influences the aims is displayed. Furthermore, the combination of all the factors which comes closest to the requested aim is shown.
Today, software is used to carry out DoE, as these provide more cost-effective results than experiments in practice.

Quality: The
DoE calculates the influence of each factor for the requested aim.
Related topics:
This glossary of plastic industry is provided by PLEXPERT Canada Inc.








